You are here
Scaffold and Support Language
The purpose of the Scaffold and Support Language section:
This section contains resources to help scaffold and support instruction for English learners.
WIDA Resources
WIDA ELD Standards Framework, 2020 Edition
Suggestions for use: The WIDA ELD Standards Framework, 2020 edition is WIDA’s newest standards resource. Grade Level Cluster materials provide example language expectations related to unit level content-area instruction and framed around the four Key Language Uses:
- Narrate
- Inform
- Explain
- Argue
Furthermore, each grade level cluster example includes other language functions that are needed to do each Key Language Use. These other language functions are stepping stones to the Key Language Use. Recognizing that teachers may require additional resources for teaching language functions, each grade level cluster example also includes example language features for teaching the language functions.
The 2020 edition is the most up to date WIDA resource and better aligns with the current content academic standards when compared with previous editions of the WIDA Standards Framework. That said, it is up to each local school/district to determine the speed with which they transition to the 2020 edition.
Citation: Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System. (2020). WIDA English Language Development Standards Framework, 2020 Edition Kindergarten – Grade 12. (Publication). Wisconsin Center for Education Research at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
2017 WIDA K-12 Can Do Descriptors, Key Uses Edition and Name Charts
Suggestions for use: The 2017 Can Do Descriptors, Key Uses Edition provides teachers with examples of differentiated instruction by grade level cluster, and by language proficiency level for the 2017 Key Uses:
- Recount
- Explain
- Argue
- Discuss
Accompanying name charts for the 2017 Key Uses provide spaces for students’ names for each 2017 Key Use, language domain, and language proficiency level. The 2017 Can Do Descriptors Key Uses may be used to help educators plan for appropriate scaffolds and supports by Key Use.
However, teachers should keep in mind that the 2017 Key Uses are not the most up to date WIDA resource, and two of the four Key Uses have changed. As Content Academic Standards (CAS) are updated, WIDA updates their resources to better align with the CAS. For this reason, the Key Uses were updated in 2020 to better reflect and support the CAS. For more information on the current Key Language Uses, see the WIDA ELD Standards Framework, 2020 Edition section above and the Functional Language webpage.
Should Not Be Used: The 2017 Can Do Descriptors Key Uses should not be used for student goal setting. The recommended resources for student goal setting are the 2020 Proficiency Level Descriptors, which are available by grade level span for the Expressive Communication Mode (Speaking, Writing, and Representing) and for the Interpretive Communication Mode (Listening, Reading, and Viewing). For more information and links to grade level span Proficiency Level Descriptors, visit the Formative Assessments webpage.
Citation: Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System. (2017) WIDA K-12 Can Do Descriptors, Key Uses Edition and Name Charts (Publication). Wisconsin Center for Education Research which partnered with The Center for Applied Linguistics.
WIDA Examples of Use of Graphic Organizers Across the ELP Standards
Figure 3J: Examples of Use of Graphic Organizers across the ELP Standards
|
ELP standard |
1- Social and Instructional language |
2- The language of Language Arts |
3- The language of Mathematics |
4- The language of Science |
5- The language of Social Studies |
|
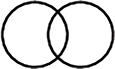
Venn Diagrams - Comparing and Contrasting Two Entities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
T-Charts - Sorting or Categorizing Objects or Concepts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cycles - Producing a Series of Connected Events or a Process |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cause and Effect - Illustrating a Relationship |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Semantic Webs - Connecting Categories to Themes or Topics |
|
|
|
|
|
Adopted from Gottlieb, M. (2006). Assessing English language learners: Bridges from language proficiency to academic achievement. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Suggestions for use: Figure 3J on page RG-23 provides examples of graphic organizers for supporting the language of each content area.
Citation: Gottlieb, M., Cranley, M. E., & Cammilleri, A. (2010). English language proficiency standards and resource guide: prekindergarten through grade 12, 2007 Edition. Madison, WI: Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of WIDA Consortium.
WIDA Sensory, Graphic and Interactive Supports
Figure 3G: Examples of Sensory, Graphic and Interactive Supports
|
Sensory Supports |
Graphic Supports |
Interactive Supports |
|
|
|
Figure 3H: Specific Examples of Sensory Supports
|
Supports related to the language of Language Arts |
Supports related to the language of Mathematics |
Supports related to the language of Science |
Supports related to the language of Social Studies |
|
Illustrated word/phrase walls Felt or magnetic figures of story elements Sequence blocks Environmental print Posters or displays Bulletin boards Photographs Cartoons Audio books Songs/Chants |
Blocks/Cubes Clocks, sundials and other timekeepers Number lines Models of geometric figures Calculators Protractors Rulers, yard/meter sticks Geoboards Counters Compasses Calendars Coins |
Scientific instruments Measurement tools Physical models Natural materials Actual substances, organisms or objects of investigation Posters/Illustrations of processes or cycles |
Maps Globes Atlases Compasses Timelines Multicultural artifacts Arial & satellite photographs Video clips |
Suggestions for use: Figure 3G on page RG-21 lists different examples of sensory, graphic and interactive supports for language learning. Figure 3H, also on page RG-21, provides specific examples of sensory supports for the language of each content area.
Citation: Gottlieb, M., Cranley, M.E., & Cammilleri, A. (2010) English language proficiency standards and resource guide: prekindergarten through grade 12, 2007 Edition. Madison, WI: Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of WIDA Consortium.

Connect With Us